Data security is a pervasive and pressing problem in the field of education today. Schools, districts, and states are encountering more and more threats to maintaining the privacy and security of their students’ data. The onset of the pandemic has only made these challenges more acute, as the immediate and universal transition to online learning drastically increased the volume and frequency of student data and digital records being created and transmitted. Nefarious actors have taken advantage of this increase, targeting at least 27 school districts in 2022 alone for security and ransomware attacks, with concerns that such attacks will only increase. This year, the two largest school districts in the US, New York City and Los Angeles, were each victims of security threats, bringing renewed attention to the urgency of shoring up educational data systems.
Since its inception, Education Analytics has been committed to using the most up-to-date technology and industry best practices to ensure the continued security of the data entrusted to us by our partners. As we’ve discussed in our blog before, data security is in fact fundamental to our mission as an organization, and data privacy is core to everything we do. We understand that our partners want to know that they can trust us with their student data and that they can feel confident we are taking every precaution we can to avoid any nefarious activity.
In light of the recent troubling trend in the field of education, we wanted to highlight one of our most recent efforts to remain on the cutting edge of data security: a process called a SOC2 audit, which involves annual IT audits by third-party auditors ensuring we adhere to the highest standards of data security.
A brief background on SOC2
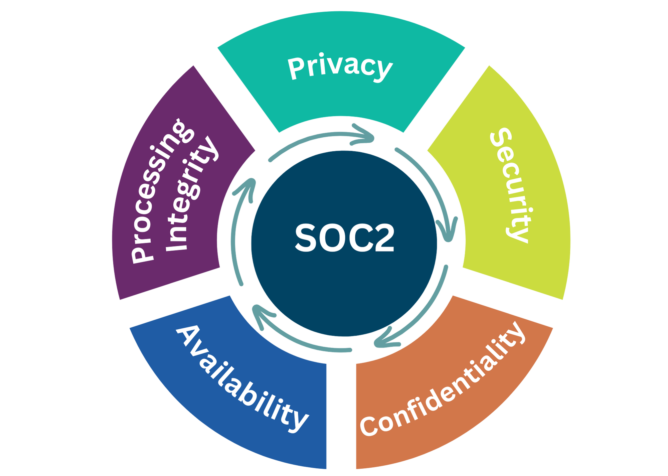
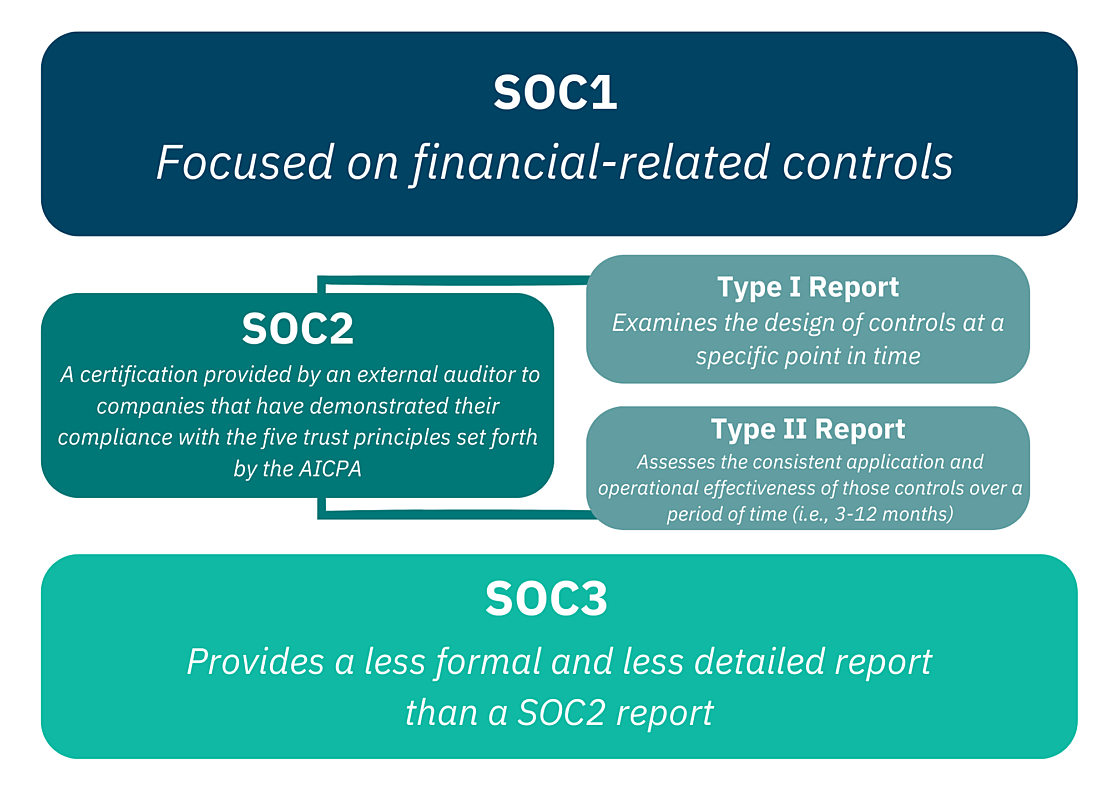
SOC stands for “System and Organizational Controls,” which means the processes (or “controls”) in place to ensure the security of an IT system or data system, as well as the security of the organization itself. SOC2 is a certification provided by an external auditor to companies that have demonstrated their compliance with the five trust principles set forth by the American Institute of CPAs (AICPA), which designed the SOC2 process. These five principles (which we discuss in more detail in the next section) are privacy, security, confidentiality, availability, and processing integrity.
SOC2 certification, achieved by successfully completing a SOC2 audit and receiving a SOC2 report, is different from SOC1, which is more focused on financial-related controls, and different from SOC3, which provides a less formal and less detailed report than a SOC2 report. There are also two types of SOC2 reports: A Type 1 report examines the design of controls at a specific point in time, whereas a Type 2 report assesses the consistent application and operational effectiveness of those controls over a period of time (i.e., 3-12 months).
We initiated the SOC2 process in 2021, when we designed the security controls that the audit would assess in 2022. Throughout 2022, we have been undergoing our first annual SOC2 audit process to test those controls in practice, and we are anticipating the receipt of our SOC2 report at the end of 2022. By undergoing the SOC2 audit process, and by sharing information about it here, we aim to help advocate for the kinds of processes and best practices that help the field of education remain cutting-edge when it comes to data security, privacy, and confidentiality.
The SOC2 criteria
As mentioned above, SOC2 is based on five trust principles: privacy, security, confidentiality, availability, and processing integrity. These five categories each cover a set of internal controls related to different aspects of the organization's information security approach. Although security is the only required criteria for SOC2 certification, EA chose to include controls that demonstrate compliance with all five criteria in our SOC2 audit.
Privacy is about securing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) collected from our partners. This category covers consent, collection, and communication of personal information. It also includes verification of IT access controls, in order to ensure that only appropriate individuals have access to PII information with a clear scope of what can be done with the data. Example controls for the privacy criteria include EA’s privacy policy, our data release agreements, IT access controls, and data encryption at rest and in transit.
Security covers protection of data and information throughout its life cycle in the organization’s workflow. Security controls protect against unauthorized access, unauthorized disclosure, or damage to systems and networks that could affect the overall security of our organization’s IT practices. Security controls are comprehensive and must include network monitoring tools that prevent or detect unauthorized activity, such as network and application firewalls and intrusion detection solutions.
Confidentiality is about demonstrating the ability to protect confidential information throughout its lifecycle at the organization, including during data collection, data processing, and data destruction. For the data that EA handles, the controls for confidentiality are defined by the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) as well as applicable state and district education laws; these controls are put in place via the Data Release Agreements and contracts we sign with our partners. Confidential information includes all intellectual property data, PII, and any other data collected as part of the data processing services provided by EA. Some key controls for confidentiality include our data destruction policy, backup, data encryption, and identity and access management. This is one of the key criteria for educational service provider organizations like EA, because we store sensitive information that is protected by FERPA and Data Release Agreements, which govern specific use and destruction of data.
Availability controls must demonstrate that the systems EA provides maintain operational uptime and performance to comply with the agreed upon Service Level Agreements with partners. This category focuses on ensuring that controls exist to maintain consistent and reliable operation of our systems. As we continue to expand our cloud-based product and service offerings, this has become a primary criterion for EA. Some key availability controls include performance monitoring, sufficient data backups, disaster recovery plans, and security incident protocols.
Processing integrity ensures that data are processed accurately and reliably and are free of errors. This category is extremely important for EA, because our partners depend on the accuracy of data processing for informing their data-driven decision making. Some processing integrity controls include change management processes, quality assurance, and processing monitoring.
EA’s SOC2 journey
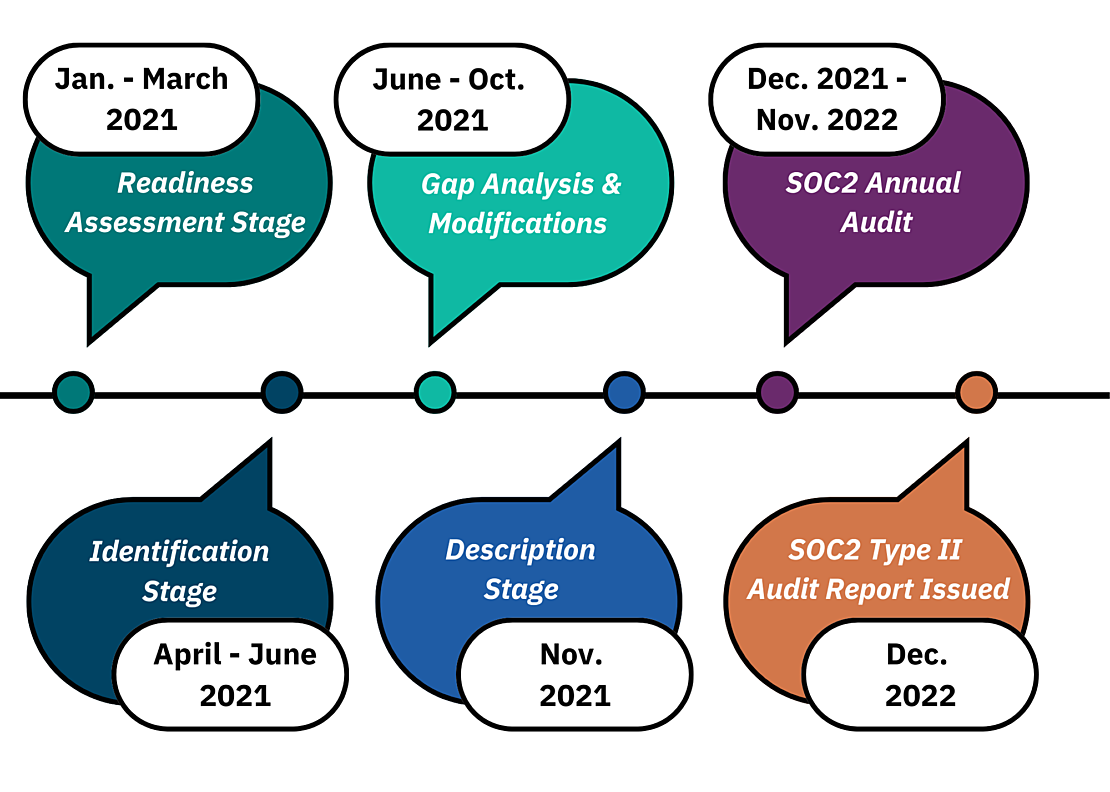
The timeline below depicts when we undertook each of the five major steps of the SOC2 process. From January to March 2021, we engaged in the Readiness Assessment Stage, where we first identified the appropriate type of audit (i.e., Type 1 vs. Type 2), defined the scope and objectives of the audit, and analyzed the areas of focus for the audit (i.e., infrastructure, data, people, processes, risk management policies, and software). This stage is also where we determined our stakeholders, meaning we identified the key people in our organization who would need to be involved in the SOC2 audit; we selected a team of SOC2 leads across the organization to support Lalanthika (as the project lead) in collecting the various controls in place for each of the trust services criteria. SOC2 leads came from many different teams at the organization:
- IT was responsible for establishing and maintaining policies pertaining to our IT systems and network, including access control and security
- Finance needed to demonstrate proof of financial controls, including financial statements and accounting policies
- People Operations was tasked with overseeing controls regarding employee management, performance improvement, organizational policies, bonus determination, recruiting practices, and role definitions
- The Office of the CEO was tasked with overseeing controls impacting organizational policy making at the executive team level and controls related to our Board and Board management
- Data Strategy oversaw controls related to partner management, data release agreements, contracts, and support ticket management processes
- The Software Engineering and Data Engineering teams ensured compliance with security standards and policies for software applications EA deploys
- Cloud Engineering and Interoperability was tasked with showing compliance with controls regarding cloud security and cloud server management
From April to June 2021, we were in the Identification Stage, where we evaluated the five trust services criteria, defined the controls and processes for each of the trust services criteria, determined the best practices and steps needed to put those controls in place, discussed and received feedback on the identified controls with the auditor, and assigned responsibility for each control to one of the SOC2 leads from the teams listed above.
From June to October 2021, we completed a Gap Analysis where we identified existing gaps in our controls and processes needing to be addressed, and we implemented Modifications based on that analysis. In other words, we implemented new controls and procedures to address any gaps identified for each of the trust services criteria, modified workflows and existing procedures as needed, trained employees on modified processes, reviewed these new controls with and received feedback from the auditor, and prepared detailed documentation of each control and the processes needed to implement each control. This gap analysis also served as an equivalent to a SOC2 Type 1 audit. Upon completion of this point-in-time audit in November 2021, the 12-month period of the SOC2 Type 2 audit began to check on the operational efficiency of these controls.
In November 2021, we also engaged in the Description Stage, where we prepared a description of the full scope of the audit (based on the previous stages completed). This description includes detailed documentation of elements such as the types of services EA provides, the components of our IT infrastructure and systems, each of the controls subject to the audit, documented system incidents, and more. This description is reviewed with the auditor and finalized based on the auditor’s feedback.
Beginning in December 2021 and lasting through November 2022, EA’s SOC2 Type 2 annual audit took place. During this stage, the third-party audit firm tested the effectiveness and operational efficiency of the controls we put in place. As the auditor reviewed the controls under each section, they captured proof of implementation for each of the controls at several points during the audit period. The auditor conducted follow-up meetings with team leads as needed for additional clarifications and to obtain log reports demonstrating compliance of the controls as described in the SOC2 report.
Finally, in December 2022, after the first annual audit, the SOC2 Type 2 audit report will be issued by the auditing firm. The report will explain each of EA’s controls and the extent to which they comply with the five trust services criteria.
What we've learned
Some of the important lessons that we learned during the SOC2 audit process have helped us in improving our process efficiency for our future SOC2 audits, while also supporting general process improvements across the organization. We share some of these lessons below, knowing that they may be helpful for any organization getting started on their SOC2 journey.
First, the most important factor to ensure a successful audit is cross-team collaboration. Multiple teams at EA were involved in identifying these controls and then providing documentation and evidence that the controls were being implemented. The SOC2 process is a multi-year journey that requires engaged involvement from all departments in the organization. It is a helpful tool for continually reemphasizing the full organization’s responsibility for ensuring high standards of data security, and it reinforces that data security lies with all teams—from the Board of Directors to the Executive Team to front-line staff.
Second, do not underestimate the time and effort required to perform the initial discovery phases of the audit process (meaning, the readiness assessment, identification, gap analysis, and description stages). Identifying the controls within each of the trust services criteria and gaining both understanding and buy-in from the stakeholders involved in the audit takes a significant amount of time—nearly a year in our case.
Third, performing a point-in-time audit before beginning the annual 12-month audit is an incredibly valuable tool for identifying gaps and avoiding surprises in the process of the annual audit. This step ensured that by the time we started the 12-month audit, we felt confident about our controls and processes in place and were not left guessing about whether we had adequately identified and implemented the necessary controls in the first place.
Finally, SOC2 Type 2 audits are about process adoption and change management to ensure regular adherence to best practices, as opposed to point-in-time audits that involve just a single check point. This has the potential to fundamentally improve the organization’s policies and practices to be in line with the highest security standards. Throughout this process, we have truly seen this mindset shift across all our teams in our first two years of our SOC2 journey from checkbox compliance to modification of workflows.
What's next for us in data security
Our final SOC2 report from our first annual SOC2 audit will be coming either later this month or in January 2023. Each year, we will repeat this process to ensure the continued operational effectiveness and efficiency of the security practices we have in place throughout our entire organization, especially as we continue to grow.
In addition, we are pursuing an additional certification, called ISO 27001. Similar in concept to SOC2, ISO 27001 is a process of defining how our organization meets the criteria set forth by ISO, the International Organization for Standardization, and undergoing an audit to ensure compliance in order to receive certification. SOC2 certification is a necessary and useful step (somewhat like a pre-requisite) towards ISO 27001 certification, which is a broader international standard for data security. We are also starting to see ISO 27001 certification emerge as a requirement in some Requests for Proposals (RFPs) from our education agency partners—a requirement we strongly support.
Data security continues to be a main priority for us at Education Analytics. You can read more about our commitment to security and privacy in our privacy policy here.